Operations are generally divided in two main groups: operations with numbers, and operations with text.
Operations are performed by considering their level of precedence. Same level operations are executed sequentially in the order they appear in the expression.
Comparisons work with any data type. When performed on text arguments, the operation is performed by comparing the ASCII codes in each argument sequentially.
Some operations have dual function depending on the type of the arguments they work with. The operator “\” for example will perform integer division when working with integer numbers. The same operator however can be used to round a real number:
x = 2.75 \ 1 ‘ this is equivalent to x = 3
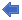
Arithmetic and logic operations
|
Operation |
Argument type |
Description |
|
+ |
any |
Performs addition with numbers Texts are concatenated |
|
- |
numeric |
Subtraction |
|
* |
numeric |
Multiplication |
|
/ |
numeric |
Division |
|
\ |
numeric |
Integer division with integer numbers With real numbers the result is rounded to the nearest integer number |
|
\\ |
numeric |
Modulo operation with integer numbers With real numbers the result is only the fraction after the decimal point |
|
^ |
numeric |
Exponentiation |
|
and |
integer only |
Bitwise AND |
|
or |
integer only |
Bitwise OR |
|
xor |
integer only |
Bitwise Exclusive OR |
|
not |
numeric |
The function is 1 if the argument is 0, and 0 if the argument is not 0 |
|
~ |
numeric |
Bitwise negation with integer numbers With real numbers only the sign of the number is inverted |
|
<< |
integer only |
Bit shift left |
|
>> |
integer only |
Bit shift right |
|
++ |
numeric |
Increment by 1 |
|
-- |
numeric |
Decrement by 1 |
The “++” and “--“ operations deserve a few extra words. These two work with numeric variables only, and immediately precede or follow in the source the variable name, on which will perform increment by 1 or decrement by 1, respectively.
When preceding the variable (as in “++a”) the operation is performed before the value from the variable is taken.
Trailing the variable (as in “a++”) means the variable value modified after it was taken in the statement.
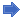
|
Operation |
Description |
|
== |
Returns 1 if the two arguments are equal |
|
<> |
Returns 1 if the two arguments are different |
|
< |
Returns 1 if argument 1 is smaller than argument 2 |
|
<= |
Returns 1 if argument 1 is smaller or equal than argument 2 |
|
>= |
Returns 1 if argument 1 is greater or equal than argument 2 |
|
> |
Returns 1 if argument 1 is greater than argument 2 |
By their level of precedence all operations are grouped in this way:
|
Operation |
Level |
|
++ -- |
highest |
|
~ not |
|
|
^ |
|
|
<< >> |
|
|
* / \ \\ |
|
|
+ - |
|
|
== <> < <= >= > |
|
|
and or xor |
lowest |
The order of execution the operations can be changed if necessary, by enclosing in ( brackets ) the needed sections in an expression.